概要
Angular2でComponent間でデータをやり取りしたい状況が出てくると思います。
例えば「このボタンを押したら外部APIを叩いて状態を更新したい。その状態を他のComponentでも使っているので更新を反映したい」ときなどです。
今回はServiceにデータを保持して、それを各コンポーネントで利用するやり方を紹介します。
環境
- angular-cli 1.0.0-beta.25.5
- Angular 2.4.3
完成形
今回の成果物はこちら
フォルダツリーは以下です。
├── app.component.css
├── app.component.html
├── app.component.spec.ts
├── app.component.ts
├── app.module.ts
├── child
│ ├── child.component.css
│ ├── child.component.html
│ ├── child.component.spec.ts
│ └── child.component.ts
├── parent
│ ├── parent.component.css
│ ├── parent.component.html
│ ├── parent.component.spec.ts
│ └── parent.component.ts
└── shared
├── data.service.spec.ts
└── data.service.ts
初期設定
ng-cliを使ってサクッと環境を用意します。
$ ng init $ ng generate component parent $ ng generate component child $ mkdir src/app/shared $ ng generate service shared/data
ServiceにObservableなSubjectを用意する
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Subject } from 'rxjs/Subject'; @Injectable() export class DataService { constructor() { } private toParentDataSource = new Subject<string>(); private toChildDataSource = new Subject<string>(); // Observable streams public toParentData$= this.toParentDataSource.asObservable(); public toChildData$= this.toChildDataSource.asObservable(); // Service message commands sendMsgToParent(msg: string) { this.toParentDataSource.next(msg); } sendMsgToChild(msg: string) { this.toChildDataSource.next(msg); } }
ポイントは
toParentDataSourceといったデータを保持する変数を用意asObservable()でsubscribe可能なpublic変数を用意next()で値を更新する(notify)するメソッドを用意
です。
親コンポーネント
親コンポーネントを以下のように作ります。
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { DataService } from '../shared/data.service'; @Component({ selector: 'app-parent', templateUrl: './parent.component.html', styleUrls: ['./parent.component.css'], providers: [ DataService ] }) export class ParentComponent implements OnInit { private msg: string; constructor(private dataService: DataService) { } ngOnInit() { this.dataService.toParentData$.subscribe( msg => { this.msg = msg; }); } sendMessage() { this.dataService.sendMsgToChild('Hello Child!'); } resetMessage() { this.dataService.sendMsgToChild(''); } }
ポイントは
providersでDataServiceをDIしているところdataServiceからtoParentData$をsubscribeしているところ
です。これによってtoParentData$に変更があった際にすぐにデータの更新を取得できます。
子コンポーネント
import { Component, OnInit, OnDestroy } from '@angular/core'; import { DataService } from '../shared/data.service'; import { Subscription } from 'rxjs/Subscription'; @Component({ selector: 'app-child', templateUrl: './child.component.html', styleUrls: ['./child.component.css'] }) export class ChildComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy { private msg: string; private subscription: Subscription; constructor(private dataService: DataService) { } ngOnInit() { this.subscription = this.dataService.toChildData$.subscribe( msg => { this.msg = msg; }); } ngOnDestroy() { // prevent memory leak when component destroyed this.subscription.unsubscribe(); } sendMessage() { this.dataService.sendMsgToParent('Hello Parent!'); } resetMessage() { this.dataService.sendMsgToParent(''); } }
ポイントは
providersでDataServiceをDIしていないところ。親で設定してあり、子で記述しなければ子は親のServiceを見ます。dataServiceからtoChildData$をsubscribeしているところ- リソースリークしないよう
ngOnDestroy()でsubscribeを止めているところ。
です。
HTML
HTMLは以下のようにします。
親コンポーネント
<div> <h1>Parent</h1> <p>Message from child: </p> <p>{{ msg }}</p> <button (click)=sendMessage()>Send msg to child</button> <button (click)=resetMessage()>Reset</button> <app-child></app-child> </div>
子コンポーネント
<div> <h1>Child</h1> <p>Message from parent: </p> <p>{{ msg }}</p> <button (click)=sendMessage()>Send msg to parent</button> <button (click)=resetMessage()>Reset</button> </div>
動作確認
初期状態
上記のコードを実行すると以下の画面が表示されます。

親から子へ
まずは親からメッセージを送ります。
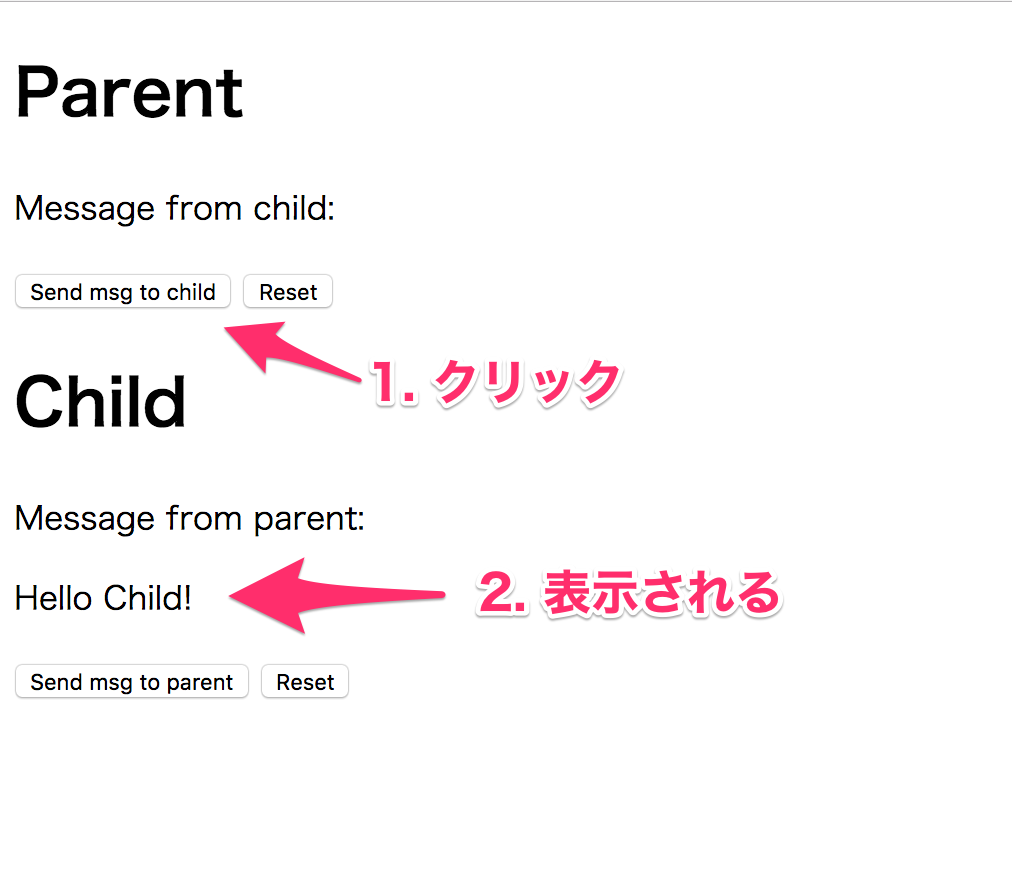
子から親へ
次に子から親へメッセージを送ります。
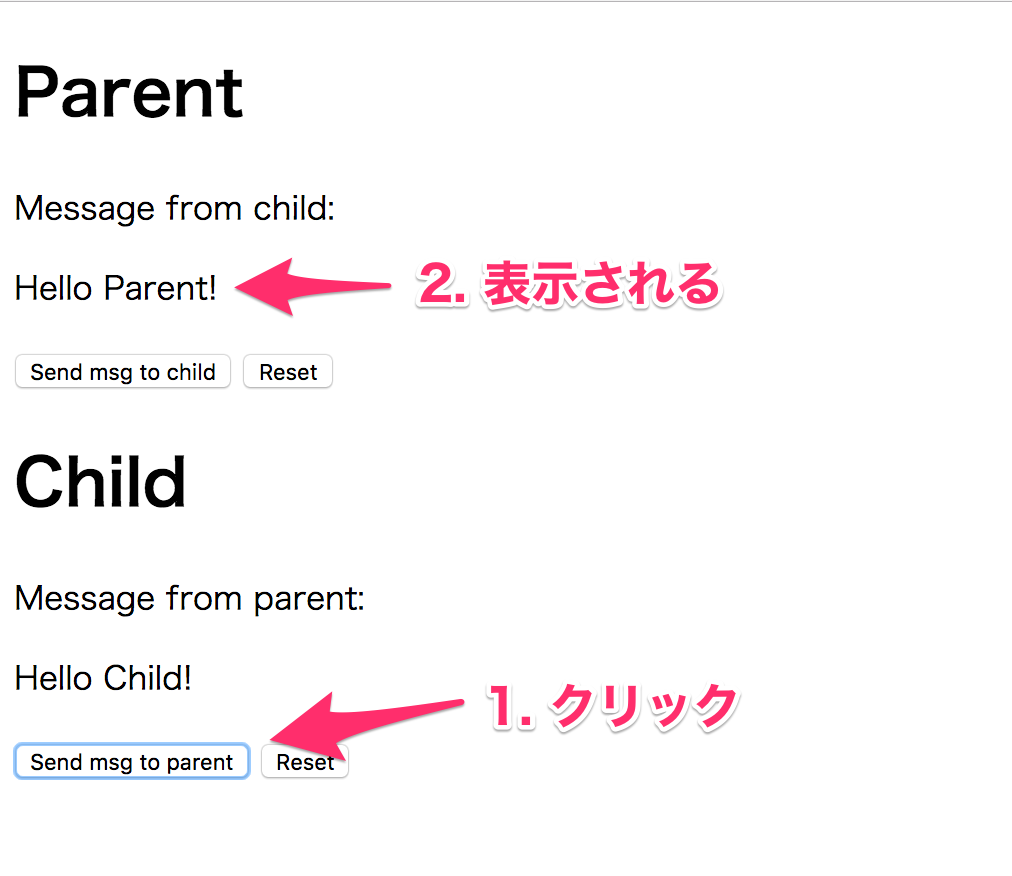
大丈夫ですね。
ポイント
DIするServiceのインスタンスがどこにあるかを把握する
Componentをまたいだデータのやり取りでは、データを保持するServiceのインスタンスを同一にする必要があります。
ここでもし子コンポーネントの方でもprovidersでDIし、インスタンスを生成してしまうと、親と子のインスタンスが異なるのでデータのやり取りができなくなります。
なぜ子コンポーネントだけunsubscribe()するのか?
また親コンポーネントではunsubscribe()せず、子コンポーネントのみしていますが、これは親コンポーネントとDataServiceのインスタンスが同じ場所にあるので、親コンポーネント自体が破棄された際にインスタンスも破棄されるので処理が不要になります。
親子でないコンポーネント間でやり取りするにはどうすればよいのか?
Serviceのインスタンスを同じにすればよいので、一番上にあるapp.module.tsのprovidersに設定すればOKです。
@NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent, ParentComponent, ChildComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule, FormsModule, HttpModule ], providers: [DataService], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { }
そうすれば各コンポーネントがそのインスタンスを見るので、そのService内で保持している変数を取得できます。
ただしこの場合、利用する各コンポーネントでちゃんとunsubscribe()する処理を入れてください。
まとめ
今回Component間でのデータのやり取りを紹介しました。
分かりやすさのため親と子では別の変数(Service内の)を扱っていますが、同じ変数をsubscribe()すればもちろん同じデータを参照できます。